Pagan Holiday Known as “St.Valentine’s Day”
http://worldtruth.tv/pagan-holiday-known-as-st-valentines-day/

The Romans celebrated a Pagan holiday on February 14th to honor Juno Fructifier, Queen of the Roman gods and goddesses as well as goddess of marriage. In one ritual, women would submit their names to a common box and men would each draw one out. These two would be a couple for the duration of the festival (and at times for the entire following year). Both rituals were designed to promote not only fertility, but also life generally.

February 15th & Feast of Lupercalia:
On February 15, Romans celebrated Luperaclia, honoring Faunus, god of
fertility. Men would go to a grotto dedicated to Lupercal, the wolf god, located
at the foot of Palatine Hill and where Romans believed that the founders of
Rome, Romulus and Remus, were suckled by a she-wolf. The men would sacrifice a
goat, don its skin, and run around, hitting women with small whips, an act which
was supposed to ensure fertility.
St. Valentine, Christian Priest:
According to one story, Roman emperor Claudius II imposed a ban on marriages
because too many young men were dodging the draft by getting married (only
single men had to enter the army). A Christian priest named Valentinus was
caught performing secret marriages and sentenced to death. While awaiting
execution, young lovers visited him with notes about how much better love is
than war — the first valentines. The execution occurred in 269 CE on February
14th.
Another Valentinus was a priest jailed for helping Christians. During his stay he fell in love with the jailers daughter and sent her notes signed from your Valentine. He was eventually beheaded and buried on the Via Flaminia. Reportedly Pope Julius I built a basilica over his grave. A third and final Valentinius was the bishop of Terni and he was also martyred, with his relics being taken back to Terni.

Christianity Takes Over Valentines Day:
In 469, emperor Gelasius declared February 14th a holy day in honor of
Valentinus instead of the pagan god Lupercus. This allowed Christianity to take
over some of the celebrations of love and fertility which had perviously
occurred in the context of paganism. Pagan celebrations were reworked to fit the
martyr theme — Christianity did not approve of rituals that encouraged
sexuality. Instead of pulling girls names from boxes, both boys and girls chose
the names of martyred saints from a box
In 313 A.D. Roman Emperor Constantine the Great legalized Christianity and ended Rome’s persecution of Christians. In 380 A.D. Christianity is made the OFFICIAL state religion of the Roman Empire. These actions not only enabled the teachings of Christianity to spread unhindered within the empire, it encouraged non-Christians to convert to the once-persecuted religion.
The pagans, however, who adopted Christianity as their religion did not
entirely abandon the traditions and practices they held before their
“conversion.” One of these traditions brought into the church was the fertility
celebration known as the Lupercalia:
“Yet the vestiges of superstition were not absolutely obliterated, and the
festival of the Lupercalia, whose origin had preceded the foundation of Rome,
was still celebrated under the reign of Anthemius.” (The Decline and Fall of the
Roman Empire by Edward Gibbons, Chapter 36, Part 3)
Western Roman Emperor Anthemius ruled the empire from 467 to 472 A.D. Mr. Gibbons goes on to state:
“After the conversion of the Imperial city (Rome), the Christians still continued, in the month of February, the annual celebration of the Lupercalia; to which they ascribed a secret and mysterious influence on the genial powers of the animal and vegetable world. “

As innocent and harmless as St. Valentine’s Day may appear, its traditions and customs originate from two of the most sexually perverted pagan festivals of ancient history: Lupercalia and the feast day of Juno Februata.
Celebrated on February 15, Lupercalia (known as the “festival of sexual license”) was held by the ancient Romans in honor of Lupercus, god of fertility and husbandry, protector of herds and crops, and a mighty hunter—especially of wolves. The Romans believed that Lupercus would protect Rome from roving bands of wolves, which devoured livestock and people.
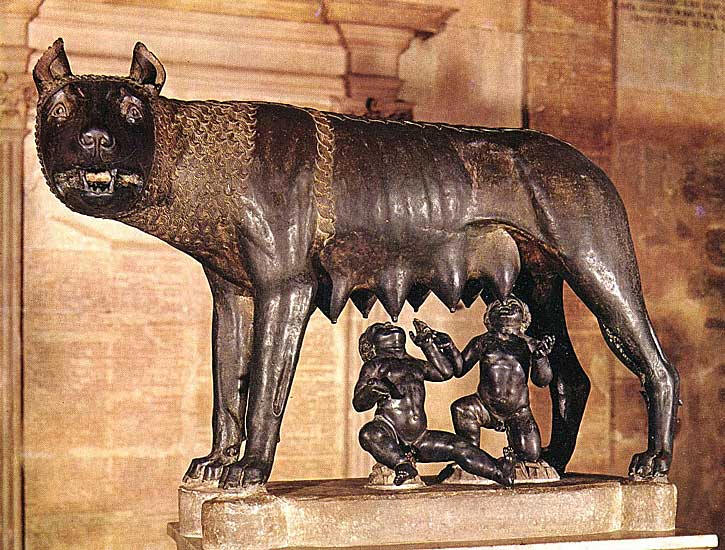

Assisted by Vestal Virgins, the Luperci (male priests) conducted purification rites by sacrificing goats and a dog in the Lupercal cave on Palatine Hill, where the Romans believed the twins Romulus and Remus had been sheltered and nursed by a she-wolf before they eventually founded Rome. Clothed in loincloths made from sacrificed goats and smeared in their blood, the Luperci would run about Rome, striking women with februa, thongs made from skins of the sacrificed goats. The Luperci believed that the floggings purified women and guaranteed their fertility and ease of childbirth. February derives from februa or “means of purification.”
To the Romans, February was also sacred to Juno Februata, the goddess of febris (“fever”) of love, and of women and marriage. On February 14, billets (small pieces of paper, each of which had the name of a teen-aged girl written on it) were put into a container. Teen-aged boys would then choose one billet at random. The boy and the girl whose name was drawn would become a “couple,” joining in erotic games at feasts and parties celebrated throughout Rome. After the festival, they would remain sexual partners for the rest of the year. This custom was observed in the Roman Empire for centuries.
In A.D. 494, Pope Gelasius renamed the festival of Juno Februata as the “Feast of the Purification of the Virgin Mary.” The date of its observance was later changed from February 14 to February 2, then changed back to the 14. It is also known as Candlemas, the Presentation of the Lord, the Purification of the Blessed Virgin and the Feast of the Presentation of Christ in the Temple.
After Constantine had made the Roman church’s brand of Christianity the official religion of the Roman Empire (A.D. 325), church leaders wanted to do away with the pagan festivals of the people. Lupercalia was high on their list. But the Roman citizens thought otherwise.
It was not until A.D. 496 that the church at Rome was able to do anything about Lupercalia. Powerless to get rid of it, Pope Gelasius instead changed it from February 15 to the 14th and called it St. Valentine’s Day. It was named after one of that church’s saints, who, in A.D. 270, was executed by the emperor for his beliefs.
According to the Catholic Encyclopedia, “At least three different Saint Valentines, all of them martyrs, are mentioned in early martyrologies under the date of 14 February. One is described as a priest at Rome, another as bishop of Interamna (modern Terni), and these two seem both to have suffered in the second half of the third century and to have been buried on the Flaminian Way, but at different distances from the city…Of the third Saint Valentine, who suffered in Africa with a number of companions, nothing is further known.” Several biographies of different men named Valentine were merged into one “official” St. Valentine.

But who was the original Valentine? What does the name Valentine mean?
Valentine comes from the Latin Valentinus, which derives from valens—“to be strong, powerful, mighty.” The Bible describes a man with a similar title: “And Cush begat Nimrod: he began to be a mighty one in the earth. He was a mighty hunter before the Lord: wherefore it is said, Even as Nimrod the mighty hunter before the Lord” (Gen. 10:8-9). He was said to have hunted with bow and arrow.
As mentioned, the Romans celebrated Lupercalia to honor the hunter god Lupercus. To the Greeks, from whom the Romans had copied most of their mythology, Lupercus was known as Pan, the god of light. The Phoenicians worshipped the same deity as Baal, the sun god. Baal was one of many names or titles for Nimrod, a mighty hunter, especially of wolves. He was also the founder and first lord of Babel (Gen. 10:10-12). Defying God, Nimrod was the originator of the Babylonian Mystery Religion, whose mythologies have been copied by the Egyptians, the Greeks, the Romans and a multitude of other ancient peoples. Under different names or titles—Pan, Lupercus, Saturn, Osiris—Nimrod is the strong man and hunter-warrior god of the ancients.
But what does the heart symbol have to do with a day honoring Nimrod/Valentine?
The title Baal means “lord” or “master,” and is mentioned throughout the Bible as the god of pagans. God warned His people not to worship or even tolerate the ways of Baal (Nimrod). In ancient Chaldean (the language of the Babylonians), bal, which is similar to Baal, meant, “heart.” This is where the Valentine heart symbol originated.
Now notice the name Cupid. It comes from the Latin verb cupere, meaning “to desire.” Cupid was the son of Venus, Roman goddess of beauty and love. Also known as Eros in ancient Greece, he was the son of Aphrodite. According to myth, he was responsible for impregnating numerous goddesses and mortals. Cupid was a child-like archer (remember, Nimrod was a skilled archer). Mythology describes Cupid as having both a cruel and happy personality. He would use his invisible arrows, tipped with gold, to strike unsuspecting men and women, causing them to fall madly in love. He did not do this for their benefit, but to drive them crazy with intense passion, to make their lives miserable, and to laugh at the results.
Many of the gods of the Egyptians, Greeks, Romans, Assyrians and others were modeled after one man—Nimrod.

The History and Significance of the god Faunus This is who you are following when you observe Valentine’s Day