
MANTOUX TB SKIN TEST UNSAFE AND UNRELIABLE
THE MANTOUX TB SKIN TEST
http://www.vaccinationinformationnetwork.com
DESCRIPTION
The TB skin test,
also known as the Mantoux test, tells if your body has been exposed to the TB
germ.
The nurse will inject a small amount of fluid just under the skin of the left
forearm.
You will see a little bubble or blister appear right away at the injection site.
This is normal and it will soon disappear.

After 2-3 days, you
will be asked to see the nurse to have the area checked and the reaction
measured.
If there is no reaction after 2-3 days, you most probably have not been exposed
to the TB germ.
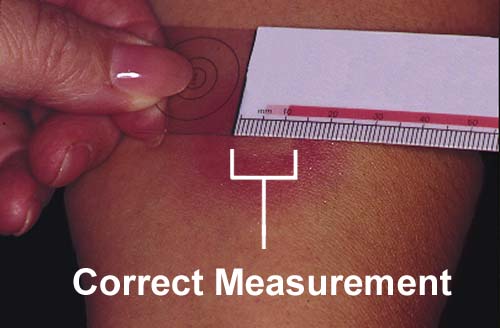
If there is a reaction, some redness and a small bump will appear on the arm.
A measurement of 10 millimetres or more is “positive”, and means you may have
the TB germ in your body.
At that point, the nurse will request additional information and tests, including chest x-ray and the collection of sputum samples. When results are abnormal, the nurse will then consult with a medical health officer who may then recommend a further course of action.
For a more detailed description, click HERE
SAFETY AND RELIABILITY
Aplisol Tuberculin contains harmful ingredients such as polysorbate 80 and phenol.
Another brand called Tubersol contains Phenol but it seems no polysorbate 80 HERE
The Mantoux test is not only harmful, but also unreliable as this paper shows:
Unreliability of the Mantoux test using 1 TU PPD in excluding childhood tuberculosis in Papua New Guinea HERE
Also read ‘Dr Len Horowitz on TB Test’ HERE
TUBERCULIN MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
Tuberculin is the fluid injected for the Mantoux Test.
Here is the Material Safety Data Sheet for a Aplisol which appears to be a commonly used brand of Tuberculin:
——————————
Aplisol® Tuberculin
Material Safety Data Sheet
(Tuberculin Purified Protein Derivative, Diluted [Stabilized Solution])
Product Summary
________________________________________
Therapeutic Area: Hospital Products
This product is distributed by: JHP Pharmaceuticals, LLC
Full Prescribing Information (NEW PI)
MSDS Sheet
Aplisol MSDS (NEW MSDS)
For additional product information please see our contact page.
Product Strength Vial
Size Unit of Sales Current NDC Previous NDC
Aplisol® (Tuberculin Purified Protein Derivative, diluted) 5TU/0.1mL 1 mL MDV 1
42023-104-01 64029-4525-1
Aplisol® (Tuberculin Purified Protein Derivative, diluted) 5TU/0.1mL 5 mL MDV 1
42023-104-05 64029-4525-2
• Equivalent to the 5
TU dose recommended as clinically established and standardized with PPD-S
• The result is read 48 to 72 hours later by a healthcare professional and
induration only is considered in interpreting the test.
DESCRIPTION
Aplisol (tuberculin PPD, diluted) is a sterile aqueous solution of a purified
protein fraction for intradermal administration as an aid in the diagnosis of
tuberculosis. The solution is stabilized with polysorbate
(Tween) 80, buffered with potassium and sodium phosphates and contains
approximately 0.35% phenol as
a pre-servative. This product is ready for immediate use without further
dilution.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Tuberculin PPD is recommended by the American Lung Association as an aid in the
detection of infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The standard tuberculin
test recommended employs the intradermal (Mantoux) test using a 5 TU dose of
tuberculin PPD.7 The 0.1-mL test dose of Aplisol (tuberculin PPD, diluted) is
equivalent to the 5 TU dose recommended as clinically established and
standardized with PPD-S. Tuberculin skin testing is not contraindicated for
persons who have been vaccinated with BCG and the skin-test results of such
persons are used to support or exclude the diagnosis of M. tuberculosis
infections.4 HIV infection is a strong risk factor for the development of TB
disease in persons having TB infection. All HIV-infected persons should receive
a PPD-tuberculin skin test.3
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Aplisol is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity or allergy to
Aplisol or any of its com-ponents. Aplisol should not be administered to persons
who have previously experienced a severe reaction (e.g., vesiculation,
ulceration, or necrosis) because of the severity of reactions that may occur at
the test site.
WARNINGS
Not all infected persons will have a delayed hypersensitivity reaction to a
tuberculin test. A number of factors have been reported to cause a decreased
ability to respond to the tuberculin test, such as the presence of infections,
viral infections (measles, mumps, chickenpox, HIV), live virus vaccinations
(measles, mumps, rubella, oral polio, varicella and yellow fever), bacterial
infections (typhoid fever, brucellosis, typhus, leprosy, pertussis, overwhelming
tuberculosis, tuberculous pleurisy), fungal infections (South American
blastomycosis), drugs (corticosteroids and other immunosuppressive agents),
metabolic derangements (chronic renal failure), low protein states (severe
protein depletion, afibrinogenemia), age (newborns, elderly patients with waned
sensitivity), stress (surgery, burns, mental illness, graft-versus-host
reactions), diseases affecting lymphoid organs (Hodgkin’s disease, lymphoma,
chronic leukemia, sarcoidosis), and malignancy.7,8,9
Any condition that impairs or attenuates cell mediated immunity potentially can cause a false negative reaction, including aging. 10,11
Tuberculin skin test
results are less reliable in HIV-infected individuals as CD4 counts decline (see
CLINICAL
PHARMACOLOGY).3
Avoid injecting tuberculin subcutaneously. If this occurs, no local reaction develops, but a general febrile reaction and/or acute inflammation around old tuberculous lesions may occur in highly sensitive individuals.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In highly sensitive individuals, strongly positive reactions including
vesiculation, ulceration or necrosis may occur at the test site; however, there
were no reports of these reactions for the period 1995 through 1998. Cold packs
or topical steroid preparations may be employed for symptomatic relief of the
associated pain, pruritus and discomfort. Strongly positive test reactions may
result in scarring at the test site. Immediate erythematous or other reactions
may occur at the injection site.
Please see the full prescribing information link above for additional information and references.
SOURCE:
 Alternative
TB Test
Alternative
TB Test

– Mantoux test reactions
Posted on the Vaccination Information Network Facebook page on 4 September 2015
Traci Leadstrom I had a horrible reaction to a TB skin test. Immune disfunction, sore and swollen joints, adrenal crash. My doctor said many people are reacting to the preservative in it. I would steer clear of the injection. Most states will allow a X-ray and doctors note.
Diedra Giles I get physically ill (vomiting/diarrhea) for 3 – 4 days after getting it. I refuse now.